Interventional neurologists use tools to access the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. They use 3D technology and advanced radiology imaging to perform medical procedures in precise ways. A common interventional neurology procedure involves threading a catheter through a patient’s groin artery to remove a blood clot. After the procedure, the blood flow to the brain resumes, and brain cells are no longer deprived of oxygen.
While interventional neurologists specialize in different disorders, they share the same fundamentals. They are trained in minimally invasive techniques and use a brain-computer interface (BCI) to treat a traumatic injury, motor neuron disease, and stroke. Interventional neurologists and other allied health care professionals are not the same, but training programs and institutions focusing on this field of medicine should emphasize the commonalities between them.
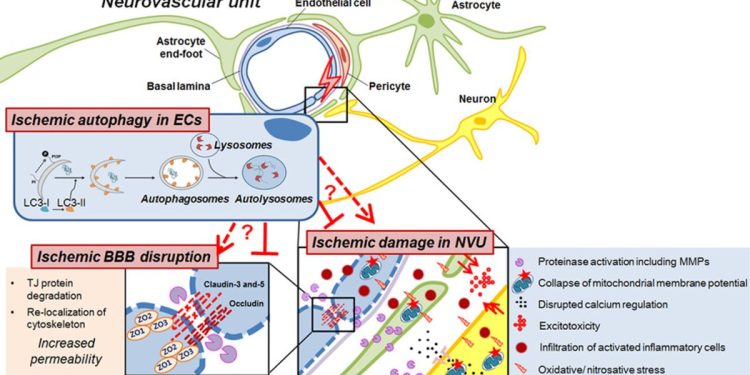
Cerebrovascular diseases are some of the most common neurological disorders and the most serious. They often have no warning signs, and they can suddenly develop into a life-threatening condition. Patients may experience significant physical and cognitive disability. These illnesses are often ischemic in nature and result in death or severe neurological disability. Some are the result of a cerebrovascular accident, while others are the result of a malformation or a brain tumor. The main purpose of an interventional neurology course is to train doctors in the various techniques used to treat such diseases.
As per report published by Coherent Market Insights, Interventional Neurology Market to surpass US$ 2.7 Billion by 2024
An interventional neurologist has special training in the use of endovascular devices. These procedures may involve the use of catheters, radiology, and other technologies. Neurovascular procedures may be used to treat conditions like stroke, ischemic stroke, and multiple sclerosis. They may also be used to repair damaged nerves and treat chronic conditions. These procedures often include minimally invasive procedures. In many cases, patients see an interventional neuroradiologist when their primary care physician fails to treat their symptoms.