Health care workers throughout the world place a high emphasis on protecting themselves to continue to help others. This procedure includes learning about infection control techniques, wearing personal protective equipment (PPE), practising excellent hand hygiene, and appropriately disposing of potentially dangerous garbage. Meanwhile, during the COVID-19 outbreak, the hazard to healthcare professionals has escalated considerably.
What Exactly Is PPE?
PPE protects the user against risks that might jeopardise their health or safety at work. It may, for example, include protective equipment such as safety helmets, eye protection, reflective clothing, and safety harnesses. Respiratory protection equipment (RPE) is also incorporated as a barrier against infectious factors such as viruses and bacteria. As such, PPE shields you against them coming into contact with your face, nostrils, eyeballs, or skin.
What Role Does PPE Play?
Employers must establish standards, policies, training, and monitoring to create a safe workplace to encourage employees to take proper precautious behaviour. Also, certain dangers may persist even when engineering controls and safe work procedures are used. So, here are a few examples of the injuries that may occur:
- Inhaling filthy air can harm your lungs.
- Objects that fall can injure the head and feet.
- Flying particles or caustic liquid spills can harm the eyes.
- Contact with corrosive substances can cause skin injury.
Hence, personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential in specific scenarios to reduce the risk.
Gear Varieties
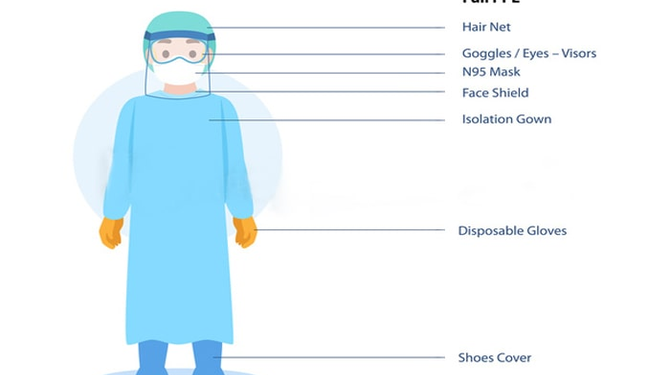
- PPE Gloves: Protect your hands from germs and help keep them clean by limiting infectious agent transmission.
- Masks: Use a mask to conceal your face and nasal passages. Meanwhile, some masks have a see-through plastic component that hides your eyes while you wear the mask (shield). A respiratory mask (respirator) covers firmly over your nose and mouth to keep pollutants out. Inhalation of microscopic organisms, such as tuberculosis bacteria, can be avoided this way.
- Eye protection: It comes in the form of face shields and goggles. These glasses can protect your eyes’ mucous membranes by keeping bodily fluids out. Meanwhile, if microbes in the fluids contact the eyes, they can enter the body through the mucous membranes.
- Clothes: Gowns, aprons, caps, and shoe covers are examples of acceptable clothing.
What to Look for While Selecting and Wearing Protective Gear (PPE)
Look for Personal Protective Gear (Enforcement) Regulations 2018 CE-marked products — suppliers may assist you with this. When choosing your choice, keep the size, fit, and weight of the PPE in mind. Consumers are more likely to use it if they are involved in the choosing process. And if you’re wearing more than one item of PPE, be sure they’re all compatible. Wearing protective goggles while wearing a respirator, for example, may compromise the seal, leading to air leakage. Also, to securely remove gloves, instruct and educate individuals on doing so without contaminating oneself. Tell them why, when, and what the tool’s limitations are.
PPE Maintenance
Protective equipment (PPE) should be stored in a dry, clean cabinet when not in use. And if it’s used again, make sure it’s clean and in good condition.
Essential Instructions for Using PPE
Having a stock of suitable disposable PPE on hand is helpful for dirty occupations when washing costs are high. For example, visitors who require protective equipment, such as respirator filters, use replacement components that match the original. Moreover, employees who use personal protection equipment must report any damage, loss, or theft to their superiors.